I'm always excited to take on new projects and collaborate with innovative minds.
say@niteshsynergy.com
https://www.niteshsynergy.com/
I'm always excited to take on new projects and collaborate with innovative minds.
say@niteshsynergy.com
https://www.niteshsynergy.com/
Here’s an outline on Nitesh Synergy blog on HTTP status codes (400, 401, 200) and HTTP methods in REST API using Spring Boot & Spring MVC. It includes use cases with real-time examples, such as employee management, gaming, teaching, and food order payments.
@RequestParam vs @QueryParam vs @PathVariable vs @PathParam
In RESTful services, HTTP status codes and methods play a crucial role in determining the success or failure of requests. Understanding how to use these correctly helps in building robust APIs. In this post, we’ll look at common HTTP status codes (200, 400, 401) and HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) in the context of Spring Boot and Spring MVC, with real-time use cases for employee management, gaming, teaching, and food order payments.
The HTTP 200 status code indicates a successful request. It’s the standard response for successful GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE requests.
In an employee management system, after adding or updating an employee, a response with a 200 OK status is sent to confirm that the request was successfully processed.
The HTTP 400 status code indicates that the server could not process the request due to client-side errors, such as invalid data or missing parameters.
In a gaming API, if a player sends an invalid move (e.g., a non-existent character ID), the server responds with a 400 Bad Request status.

HTTP 401 status code means the client is unauthorized to access the requested resource, typically due to missing or invalid authentication.
In a teaching platform API, a teacher or student attempting to access resources without being logged in would get a 401 Unauthorized status.

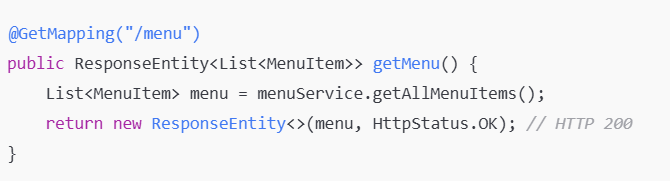
The GET method retrieves data from the server.
In a food order system, retrieving a list of menu items using a GET request.
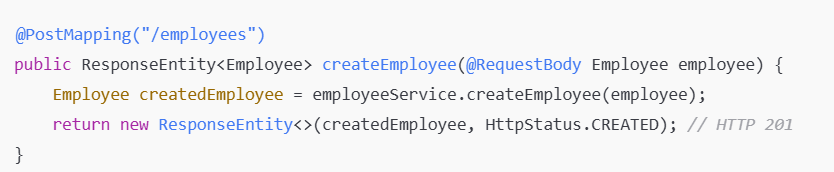
The POST method is used to send data to the server, such as creating a new record.
Creating a new employee record.
The PUT method is used to update an existing resource.
Updating a player’s status in a game.

The DELETE method is used to remove a resource from the server.
Deleting an item from a customer’s food order.


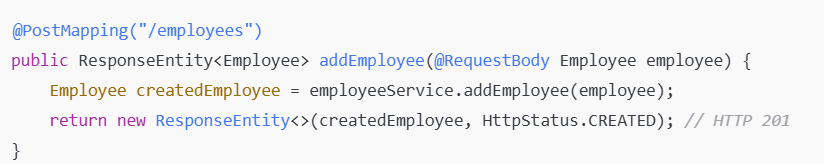
The HTTP 201 status code indicates that a request has been successfully processed and resulted in the creation of a new resource.
When an employee is successfully created, return a 201 Created status.
The HTTP 202 status code indicates that the request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed.
When a game action is initiated, but not completed yet (e.g., a server-side action like saving game progress), return HTTP 202.

The HTTP 203 status code indicates that the response metadata is not from the origin server but from a local or third-party copy.
In an online teaching platform, if course data is fetched from a cached version, this status code may be used.

8.HTTP 204 – No Content
The HTTP 204 status code indicates that the request has been successfully processed, but there is no content to return.
When a food order is successfully updated (e.g., a customer changes their delivery address), return HTTP 204 No Content.

The HTTP 301 status code indicates that the resource requested has been permanently moved to a new location.
If a food delivery address API has moved to a new endpoint, this status code is returned.

10.HTTP 302 – Found (Temporary Redirect)
The HTTP 302 status code indicates that the resource is temporarily located at a different URI.
If a player's request is temporarily redirected to a new game server for load balancing.

11.HTTP 400 – Bad Request
This indicates that the request could not be understood or was missing required parameters.
If a customer places an incomplete order (missing item details), return HTTP 400.

This status indicates that the request lacks valid authentication credentials.
A student or teacher attempting to access course content without being logged in should receive this status.

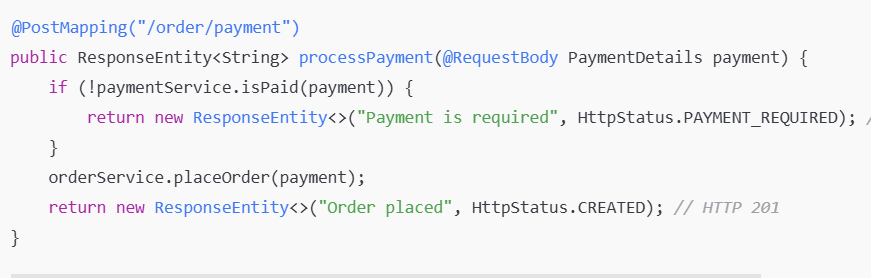
This status code is not widely used, but it could indicate that payment is required to proceed with the request.
In a food ordering system, the user is asked to pay before placing an order.
This status indicates that the server understands the request but refuses to authorize it.
If a user tries to access restricted courses they don't have permission for, return HTTP 403.

This status indicates that the requested resource could not be found.
When an employee with a specific ID does not exist in the system.

This indicates that the server encountered an unexpected condition that prevented it from fulfilling the request.
When there’s an unexpected error in the game server (e.g., database failure).

This status code indicates that the server received an invalid response from the upstream server.
If a food payment gateway returns an error, a 502 Bad Gateway status could be returned.

@RequestParam vs @QueryParam vs @PathVariable vs @PathParam
Here's a comparison of the four annotations commonly used in Spring and JAX-RS (Java API for RESTful Web Services) for extracting parameters from a request:
@RequestParam (Spring Framework):
Typically used for GET requests with URL parameters or form submissions.

2. @QueryParam (JAX-RS):
@RequestParam in Spring but used in JAX-RS (used in frameworks like Jersey or RESTEasy).
URL: /employees?department=HR
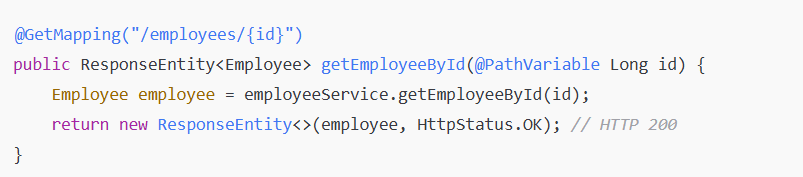
3. @PathVariable (Spring Framework):
Used to extract variables from the URI path, typically used with RESTful endpoints where the parameter is part of the URL path.
Commonly used with dynamic URIs like /employees/{id}.

4. @PathParam (JAX-RS):
Similar to @PathVariable in Spring but used in JAX-RS.
Extracts parameters from the URI path.


| Feature | @RequestParam (Spring) | @QueryParam (JAX-RS) | @PathVariable (Spring) | @PathParam (JAX-RS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Framework | Spring MVC / Spring Boot | JAX-RS (Jersey, RESTEasy, etc.) | Spring MVC / Spring Boot | JAX-RS (Jersey, RESTEasy, etc.) |
| Usage | Used to extract query parameters or form data from the URL or body | Extracts query parameters from the URL | Extracts values from the path of the URL | Extracts values from the path of the URL |
| HTTP Methods | Typically used in GET, POST, PUT, DELETE (for query/form data) | Typically used in GET, POST, PUT, DELETE (for query data) | Typically used in GET, POST, PUT, DELETE (for dynamic path segments) | Typically used in GET, POST, PUT, DELETE (for dynamic path segments) |
| Type of Parameter | Query parameters or form parameters | Query parameters | Path parameters (part of the URL) | Path parameters (part of the URL) |
| Example URL | /employees?department=HR | /employees?department=HR | /employees/123 | /employees/123 |
| Method Example | public List<Employee> getEmployees(@RequestParam String department) | public List<Employee> getEmployees(@QueryParam("department") String department) | public Employee getEmployeeById(@PathVariable Long id) | public Employee getEmployeeById(@PathParam("id") Long id) |
| Annotation Placement | Can be used with method parameters in controller classes | Can be used with method parameters in JAX-RS resource classes | Can be used with method parameters in controller classes | Can be used with method parameters in JAX-RS resource classes |
| Default Value Support | Supports default values using defaultValue attribute | Supports default values using defaultValue attribute | Does not support default values | Does not support default values |
| Required/Optional | Default is required, but can be made optional using required = false | Default is required, but can be made optional using defaultValue | Always required if the path is dynamic | Always required if the path is dynamic |
| Common Use Case | For handling form data or query parameters like search filters or pagination | For handling query parameters in RESTful web services | For handling resource identifiers in RESTful web services | For handling resource identifiers in RESTful web services |
@RequestParam / @QueryParam: Extract query parameters, often for filters, search criteria, or form data (e.g., ?page=1&size=10).
@PathVariable / @PathParam: Extract path parameters, commonly used for dynamic resource identifiers (e.g., /employees/{id}).